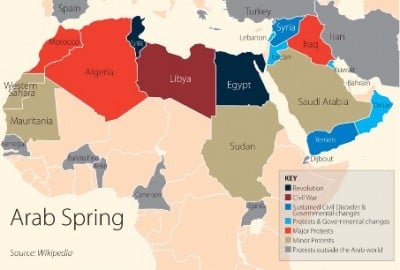
From Libya and Egypt to Syria and Yemen, the Middle East North Africa (MENA) region is undergoing unprecedented tumult and chaos. To understand the current breakdown of states and society, examining the so-called Arab Spring of 2011 that laid the groundwork for this ongoing regional anarchy is indispensable.
Global Research brings to the attention of its readers the newly released book by Christopher L. Brennan. Fall of the Arab Spring: From Revolution to Destruction (available here), propounds an incisive and timely analysis. The book views this widespread Arab upheaval, not as authentic grass roots movements for democracy, but as a US-engineered destabilization. Below are excerpts largely from the introduction.
* * *
From 2011 to around early 2014, the so-called “Arab Spring” encompassing the MENA (Middle East North Africa) region came to the forefront of international political affairs. In the words of Sergei Lavrov, Russian Foreign Minister, it was “frequently referred to as the most remarkable episode in the international life of the new 21st century.” The authoritarian regimes of the Arab world have been fragile systems. This is especially true more recently in their relationship with burgeoning youthful populations. Arab historian Said K. Aburish argues that these various regimes all lack modern political legitimacy—from Saudi Arabia and the Gulf states to Egypt, from military cliques to monarchies. [1]
This lack of modern political legitimacy—coupled with decades of political repression, world economic crises, and unresolved grievances such as the unmitigated oppression of the Palestinian people—creates potential for massive political awakening. This dynamic was particularly pronounced because of the region’s marked demographic ‘youth bulge.’
Historically, youth cohorts are receptive to new ideas, eager to challenge the status quo, and active in times of political crisis. Indeed, it was the age 25 and under demographic that spearheaded the MENA mass protests. Using what is referred to as ‘civilian-based power,’ Western powers exploited and guided this massive potential for political awakening to advance Western and Israeli geopolitical imperatives. These eruptions were followed closely by covert and overt military intervention.
[To order book click image right]

Fall of the Arab Spring: From Revolution to Destruction examines modern imperialism vis-à-vis the so-called ‘Arab Spring.’ This widespread Arab upheaval takes place in the context of a period when the restructuring of the world order—from unipolarity (uncontested world hegemony) toward multipolarity (multiple centers of power)—converges with aggravated economic breakdown. This provides the lens from which this study is viewed. The focus of this analysis is the underlying themes, methods, and most prevalent aspects of the MENA uprisings. Particular focus is given to Egypt and Libya as highly instructive case studies. Egypt demonstrates an effective utilization of ‘civilian-based power,’ while Libya provides one of the most palpable displays of the empire’s ruthless stewardship of the “Arab Spring” to smash a recalcitrant Arab state.
In his study The Sorrows of Empire, author Chalmers Johnson, professor emeritus of the University of California, San Diego, categorizes modern imperialists into two groups: “those who advocate unconstrained, unilateral American domination of the world (couched sometimes in terms of following in the footsteps of the British Empire) and those who call for imperialism devoted to ‘humanitarian’ objectives…. The complex issue at the heart of liberal imperialism is ‘humanitarian intervention’ … ‘the responsibility to protect’”[2] as a pretext for military intervention.
‘Liberal imperialism’ has continued to evolve. A more novel method for modern imperialism includes the use of the ‘color revolution.’ Adherents of this method, such as Peter Ackerman of the Albert Einstein Institute (AEI) and Carl Gershman of the National Endowment for Democracy (NED) (See Chapter II), argue unfriendly regimes can be toppled by mobilizing swarms of discontented adolescents, via mass communication media such as SMS, Facebook and Twitter. Illustrating its appeal to the Obama team, this later tactic of ‘civilian-based power’ was utilized as the initial driving force of the so-called ‘Arab Spring,’ and was later superseded by direct military intervention and America’s newest unconventional model of warfare.
Despite evidence to the contrary, the mainstream narrative is that the wave of uprisings against the status quo autocratic Arab regimes were entirely organic. Additionally, a narrative sometimes found in alternative media is that these uprisings were initially organic, but were subsequently hijacked or diverted by the West and Gulf state monarchies. The latter narrative is given credence through the West’s direct military intervention to topple Muammar Qaddafi’s government in Libya. Both of these notions are specious. The idea that romantic Arab youth activists alone initiated the attempt to topple their autocratic regimes is a myth. The objective of Fall of the Arab Spring is to shatter this prevailing mythology.
In truth, the so-called “Arab Spring”which swept through the MENA region was a wave of destabilizations sponsored by Washington and launched through ‘civilian-based power’ techniques. It was American imperialism of the most modern form. With the onset of multipolarity—with many of Washington’s vassals looking to resurgent power centers such as Moscow and Beijing—the US moved pre-emptively for ‘regime change’ against the independence of ‘enemy’ states and erstwhile clients. Additionally, the ‘Arab Spring’ offensive was given impetus by the imperative to accelerate the regional process of what Bernard Lewis, perhaps the most influential British Arabist, termed “Lebanonization” as a self- fulfilling prophecy. [3] This refers to the far-reaching balkanization, societal breakdown, and explosion of sectarian conflicts following the attenuation or collapse of the state—the model of Somalia.
For the casual outside observer, especially those imbibing the corporate controlled media’s narrative, the complex and covert nature of the destabilization meant its intrinsic imperialism was not immediately discernable. The initial lack of overt military offensives gave the empire’s use of ‘civilian-based power’ the verisimilitude of meritorious organic grassroots movements for change.
While it is important to acknowledge and support the aspirations of peoples toward accountable and democratic forms of governance, it is unacceptable to interfere in the internal affairs of sovereign states during this process. This principle is enshrined in the charter of the United Nations and that of natural law. In a non-Hobbesian world it would be recognized that is not for any state to dictate another’s government for their own selfish aggrandizement or hegemonic interests. It would be recognized that every nation has the right to determine its future independently, without outside interference. Alas, rather than this notion as a guiding principle, the Post-Cold War era unleashed a state of uncontested world hegemony by a single power: the United States. In this single world power framework its own interests and ideology are regarded as paramount.
Although it is commonly thought to have gradually faded following World War II, imperialism continues via neo-colonialism.The actions of the West, with its leading state the US at the forefront, have followed an imperialist tendency throughout the Arab uprisings. As we shall see, the West’s ongoing involvement in the “Arab Spring” is part of a larger offensive to maintain the status quo of Western and Israeli hegemony. This was done—not through the crude and direct means of the Bush II regime—but more indirectly and via a sustained synergy of hard and soft power: so-called ‘smart power.’ This was supplemented and spearheaded through the techniques of the ‘color revolution.’ Thus, although a new cadre emerged with the onset of the Obama regime, the status quo imperative to secure Israel remained, and Obama administration introduced new techniques of projecting power. Whereas the second Bush administration was blunt and bellicose, the Obama regime acted more indirectly and surreptitiously, often relying on local proxies and ambitious regional powers such as Qatar and Turkey. This approach can be aptly labeled ‘imperialism on the cheap.’ It has been the defining foreign policy strategy of the Obama presidency.
The excessive reliance on ‘hard power,’ overt military and economic means to project power, during the George W. Bush presidency, generated widespread discourse on its imperial nature.[4] In contrast, the presidency of Obama was rarely, if ever, characterized in similar terms in its early stage. On the contrary, it was often branded as a radical departure from the aggressive tendencies of the Bush II regime. ‘Soft power’ is defined as “the ability to obtain the outcomes one wants through attraction rather than using the carrots and sticks of payment or coercion.”[5] After President Bush put US standing in a compromised position—with allies antagonized and a military and populace demoralized—the American establishment opted to shift to a more emphatically ‘soft power’ approach, as advanced by theoreticians such as Joseph Nye, Jr. and Zbigniew Brzezinski of the elite Trilateral Commission. The new strategy rejected an outright bellicose use of ‘hard power,’ the proclivity of the Bush II regime. Instead, ‘hard power’ was used more selectively and from the standpoint of ‘leading from behind.’ This means encouraging allies (or vassals) to engage in geopolitical initiatives for the US, which provides necessary military aid covertly.
During the MENA uprisings, as the Trilateral Commission’s Joseph Nye had suggested even before Obama was elected, the US used “a smart strategy that combines hard- and soft-power resources—and that emphasizes alliances and networks that are responsive to the new context of a global information age.” Or, as articulated by Obama State Department apparatchik Susanne Nossel, a strategy of “enlisting others on behalf of U.S. goals, through alliances, international institutions, careful diplomacy, and the power of ideals.”This encapsulates US strategy to topple and destabilize non-compliant states during the ‘Arab Spring.’
Reacting to a waning American empire and a need to ensure the security of Israel, this synergy of ‘soft power,’ alliances, and ‘hard power’ came to characterize US strategy. In Libya—where direct military intervention took place—humanitarian imperialism was carried out with these as guiding principles. Fall of the Arab Spring outlines the synergy between this array of methods including the use of information and irregular warfare. In the final outcome, for the Arab world, the romantic illusions of ‘democracy’ and ‘dignity’—platitudes sold by the West—were shattered, and much of the region degenerated into the breakdown of the state and society.
Notes
[1] Said K. Aburish. A Brutal Friendship: The West and the Arab Elite, (New York: St. Martin’s Press), 13.
[2] Chalmers Johnson, The Sorrows of Empire: Militarism, Secrecy, and the End of the Republic, (New York: Metropolitan Books), 67.
[3] “
Another possibility, which could even be precipitated by fundamentalism, is what has of late become fashionable to call ‘Lebanonization.’ Most of the states of the Middle East—Egypt is an obvious exception—are of recent and artificial construction and are vulnerable to such a process. If the central power is sufficiently weakened, there is no real civil society to hold the polity together, no real sense of common national identity or overriding allegiance to the [nation-state]. The state then disintegrates—as happened in Lebanon—into a chaos of squabbling, feuding, fighting sects, tribes, regions and parties.”
Bernard Lewis, “Rethinking the Middle East,” Foreign Affairs, Fall 1992, http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/48213/bernard-lewis/rethinking- the-middle-east
[4]
See, for example, Michael Cox. “Empire, Imperialism and the Bush Doctrine.” Review of International Studies 30, no. 4 (2004): 585-608. http://search. proquest.com/docview/204970875?accountid=12387; Lewis H. Lapham, Pretensions to Empire: Notes on the Criminal Folly of the Bush Administration (New York: New York Press), 2007; Madeline Bunting “Beginning of the end: The US is ignoring an important lesson from history – that an empire cannot survive on brute force alone.” The Guardian, http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2003/feb/03/usa. comment ;Johnson, Empire, 322-323.
The original source of this article is Global Research













No comments:
Post a Comment